
Aravind Business Model
Eradicating needless blindness in India
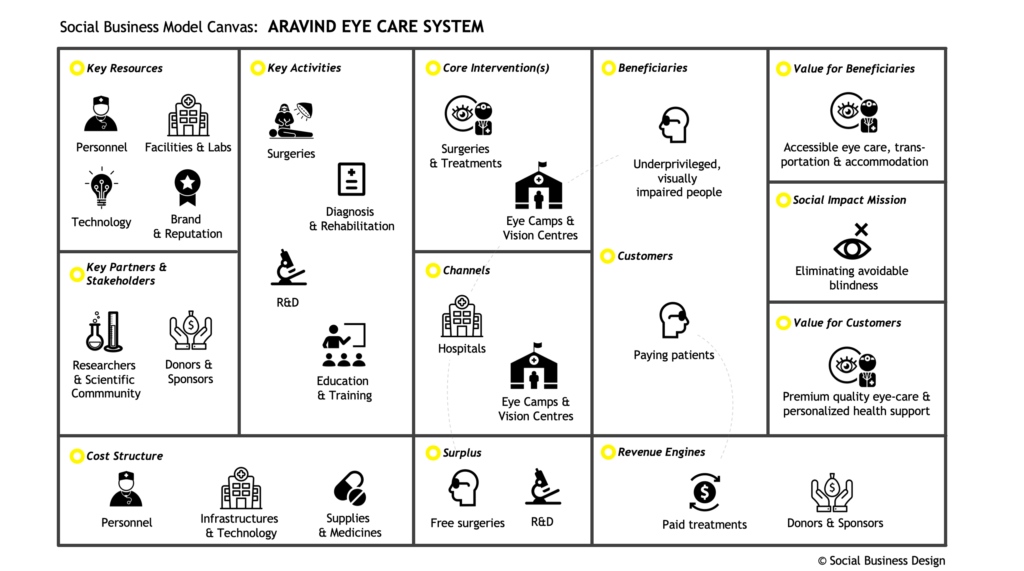


Social Impact Mission
As discussed in the introduction, since its early days Aravind’s impact goal has been to eradicate needless, avoidable blindness. To quote their vision statement, Aravind “provide compassionate and quality eye care affordable to all“. This is indeed the firm’s ultimate mission.
Beneficiaries
We might say that Aravind supports visually impaired people of all kinds. However, true primary beneficiaries are underprivileged Indians who cannot afford to pay for treatments. In fact, Aravind seeks to make sure every visually impaired person can get access to proper care, regardless of their ability to pay for it. So, this is their actual beneficiary target.
Core Interventions + Channels
Aravind’s core interventions can be divided into two main categories. On one hand, Eye Camps and Vision Centres help reach out to people in cities, suburbs and rural areas, and then diagnose eye diseases. On the other one, Hospitals and Clinics are the places where surgeries and treatments are performed. All these physical locations can be also considered as primary touchpoints and channels used by Aravind.



Value for Beneficiaries
As repeatedly mentioned, Aravind makes eye care completely accessible for its beneficiaries. Besides eye surgeries performed free of charge, people coming from rural areas also receive free transportations as well as accommodation. Furthermore, experts agree that restored sight can lead to increased social inclusion and participation in work activities.
Customers + Value for Customers
As said, Aravind supports visually impaired people of all kinds, including those who are able to pay for the surgeries. As a consequence, such patients have to be considered Aravind’s true customers. Similarly to beneficiaries, the value proposition provided consists in high quality treatments and health assistance, with personalized solutions for those who decide to pay premium prices.
Key Activities
When it comes to Aravind’s strategic activities, surgeries, diagnosis and rehabilitation procedures surely come first. Moreover, Aravind runs research activities (to improve its treatments) and runs manufacturing facilities (to produce intra-ocular lenses). Last but not least, through its training programs, Aravind manages educational activities for national and international health care operators.
Key Resources + Key Partners & Stakeholders
Given the nature of its interventions, Aravind most important internal resources are personnel (surgeons, nurses, etc.), infrastructures (i.e. clinics, hospitals, etc.) and facilities (machines, technologies, etc.). Because of its worldwide reputation, Aravind brand might be considered a key asset too. Lastly, many partner organizations, both from profit and non-profit sector, support Aravind providing additional external resources, such as IT expertise, scientific knowledge and financial support.



Cost Structure
We could spend hours discussing about Aravind cost structure. Yet, in order to quickly highlight Aravind’s major costs, we cannot forget to mention staff costs, infrastructure and equipment maintenance, as well as supplies and medicines. If interested, you can find further details inside Aravind annual report.
Revenue Engines + Surplus
As we have seen before, Aravind revenue model is based on a customer segment cross-subsidization. Moreover, sponsors and private donors contribute to generate additional income streams, which are then re-invested in free surgeries for underprivileged patients and in R&D activities.



Conclusion
Ever since its inception, Aravind has worked with more than 300 hospitals worldwide (from Latin America, Africa and Asia) and helped them replicate its model. According to Community Eye Health (2014), a successful replication mostly depends on: 1) reaching out people in need, both in urban and rural areas, regardless of their ability to pay; 2) using efficiently scarce resources and optimizing tasks and processes; 3) ensuring great user journeys and offering premium quality services and treatments; 4) creating hybrid revenue models without forgetting to fuel in donations.
In conclusion, we can say that quality eye care services, efficient workflows, hybrid revenue model and most importantly constant innovation are the key factors that made Aravind what it is today.



About the Author
Marco Cornetto
Hi, there!
I’m Marco, an Italian business practitioner with previous study and work experiences across Australia, Netherlands, Spain and Vietnam. Having a background in economics and business management, since 2018 I’m happy to support social entrepreneurs and impact startuppers refine their businesses and scale social impact.
At Social Business Design, I mostly write about business design, financial modeling and growth hacking, sharing useful tools and insights gathered during 5+ years of on-field experiences.
Apart from talking about social business, I love hiking, reading, eating Asian food and taking pictures while I’m traveling. If interested, feel free to get in touch with me through my channels! 🙂
Did you like this article?
If so, then don’t forget to check out for more at Social Business Design .